The content of the article
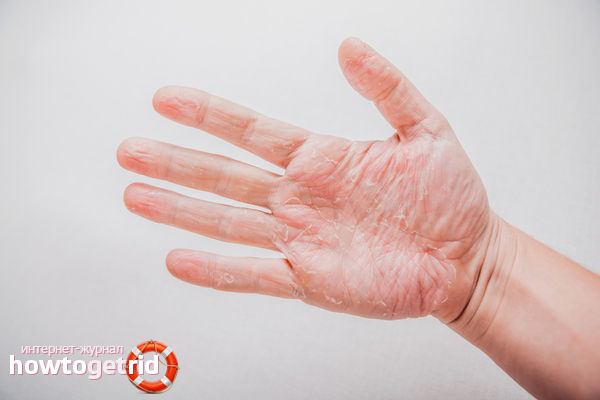
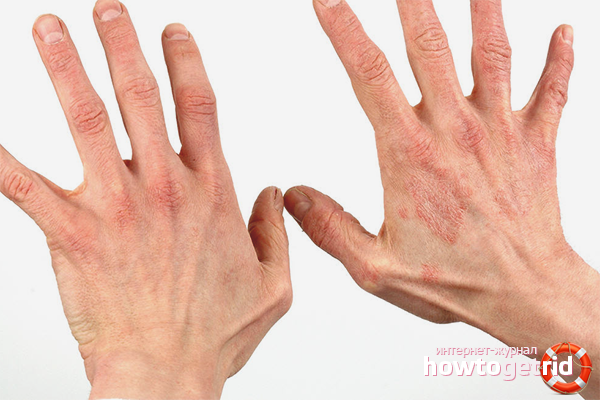
Eczema is a dermatological disease in which the skin becomes inflamed in open areas. Most often these are hands, face, feet. First, the skin turns red, a rash, burning and severe itching appear. Eczema is small vesicles that open after ripening and a wet wound appears. Eczema is very common, as it accounts for almost half of all dermatological diseases.
Patients with this diagnosis experience not only physical, but also psychological discomfort, as open wounds often seem scary and contagious to others. But in fact, eczema is not contagious. When an infected bacterium enters healthy skin, most often no changes occur; very rarely, minor rashes may appear. In order to get eczema, you need to have a number of predispositions. The complexity of the disease is that eczema is very difficult to cure completely. Its course passes cyclically - the period of exacerbation is replaced by remission. The fact that eczema returns again and again is depressing and many patients are wondering if eczema can be eliminated forever.
Causes of eczema on the hands
Eczema still refers to diseases, the exact causes of which even doctors do not know. But there are people who may be at risk. For example, eczema in the vast majority appears in allergy sufferers. This suggests that people with weak immunity who are not able to withstand some external factors have a serious predisposition to this kind of disease. Also provoking factors can be frequent contact with caustic chemicals, synthetic clothing, low-quality detergents - powder, soap, dishwashing gel.
Eczema can occur against the background of prolonged use of certain drugs, for example, uncontrolled intake of paracetamol, analgin. Some people are allergic to metal, so wearing metal objects in contact with the skin (jewelry, eyeglass frames, badges from belts) can also cause eczema on your hands. Any allergic reactions (to food allergens, to pollen of plants) can also cause a dermatological ailment.
Most often, eczema arises from professional activity, when a person, due to his specialization, encounters constant contact with caustic substances. It can be at paint and varnish factories, it can be at hairdressers (if they carry out the procedure of dyeing hair without gloves), as well as in various chemical processes.
Parasites living in the body reduce immunity, therefore, are also a provoking factor. In addition, it has been scientifically proven that nervous shocks, depression and stress stimulate the process of exacerbation of the disease, so this condition of a person can also be attributed to the causes of eczema on the hands.
Varieties of eczema and their manifestations
Depending on the form of the disease, eczema is divided into several groups.
- True (idiopathic) eczema is characterized by rashes of small acne on a fairly large area of the skin. Over time, the bubbles burst, and an inflamed, weeping tissue remains on the skin. Then the upper layer of the skin dries up, crusts form, although the inflammatory process continues on the lower layers. Such eczema is characterized by severe itching.
- Microbial eczema.It is characterized by the formation on the skin of small pustular acne and inflammation, which are of fungal or bacteriological origin. Often microbial eczema occurs at the site of open wounds, burns, cuts, abrasions, fistulas when pathogenic microbes get into unprotected tissues.
- Mycotic eczema is an allergic reaction to a fungal pathogen. A common cause of the disease is ringworm, condiasis and other types of mycoses.
- Seborrheic eczema occurs in people with seborrhea. Most often, foci are localized on the head, in the inguinal folds, behind the auricles (that is, in places of increased secretion of sebaceous fat). On the hands of such eczema rarely appears.
- Occupational eczema occurs due to constant contact with aggressive chemicals.
- Dyshidrotic eczema most often occurs on the palms and soles of the feet. Since the skin in these areas is rather thick, inflammation is rarely acute. With such eczema, groups of pustular inflammations appear, which either burst or dry up when closed.
In addition, there are such types of eczema as tilotic, varicose and sikizifornaya. There is also childhood eczema, which is almost always localized on the face - cheeks, forehead.
It is very important to accurately determine the class of eczema, as treatment may vary slightly. To do this, it is better to consult a doctor for the correct diagnosis. Regardless of what kind of eczema your doctor diagnosed, you need to treat it comprehensively. The principles of general treatment include drug therapy (both internal and external), strengthening immunity, normalizing the intestines, dieting, as well as the implementation of basic hygiene standards. We will talk about each treatment item in more detail.
Medication for eczema
This is the basis of complex treatment, because without normalization of internal resources it is impossible to defeat eczema. Here are a few areas in which the doctor acts to defeat the disease with you.
- Sorbents. Since one of the common causes of eczema is allergy, sorbents are often prescribed to the patient. Once in the intestines, they absorb the allergen, not allowing it to cause an organism reaction. Among them can be identified Filtrum, Polysorb, Enterosgel and others.
- Sedatives. If the appearance of eczema is associated with neurological disorders, treatment is often accompanied by the use of sedative drugs. They normalize the nervous system and protect the patient from sudden attacks of aggression. Among the most harmless sedative drugs are Novopassit, Persen, tincture of valerian and motherwort.
- Hormones. Some hormonal drugs (corticosteroids) are very effective against various kinds of dermatological diseases, but they have a number of contraindications. Such drugs are prescribed only by a doctor, are taken according to a scheme with gradual cancellation. In no case should you take hormones uncontrollably and often. For the treatment of eczema use prednisone, triamcinol, dexamethasone.
- Antihistamines. They are an essential component of treatment. Tsetrin, Zodak, Zirtek, Claritin, Ketotifen help relieve tissue swelling, reduce itching and burning.
- Antibacterial agents. With microbial eczema, antibiotics should be included in the treatment. It is best to take a swab or scraping from the wound and make a sowing tank, revealing against which antibiotics the microbes are the least sensitive.
- Beneficial bacteria. To normalize the intestines and protect the body from dysbiosis, they take various probiotics that sow pathological bacteria and colonize the intestines with beneficial microorganisms. Among them are Hilak Forte, Linex, Bifiform, Lactobacterin, etc.
In addition, vitamins and immunomodulators are prescribed to the patient to strengthen immunity, since the restoration of the body's defenses is the basis of recovery.
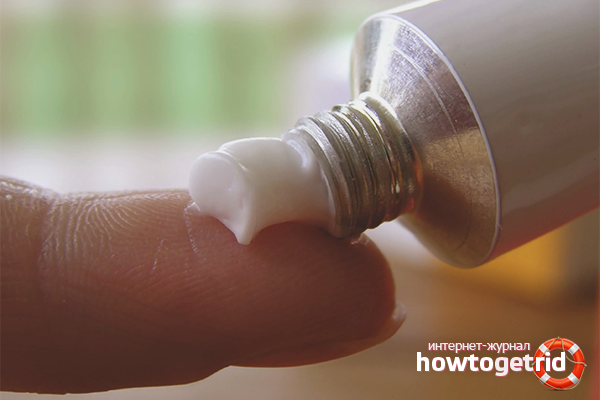
External treatment of eczema
It is very important to treat eczema not only from the inside, but also from the outside. To do this, the patient is prescribed ointments and gels with corticosteroids, which relieve itching, burning and inflammation. Among the most inexpensive, Prednisolonum, Astroderm, Hydrocartisone ointment can be distinguished. Bepanten and Panthenol will also help relieve itching and redness, these are more gentle and safe ointments that are used for minor eczema.
To relieve itching and relieve inflammation, you can use Burov's liquid, lead water, a solution of citric acid, a menthol solution. Lotions or baths are made of liquid. At home, you can use talcum powder, starch, zinc powder to dry weeping tissues.
In addition, eczema can be physiologically treated. The most common procedure is ultrasound irradiation to disinfect the wound from germs.
Hygiene for Eczema
Hygiene is another fundamental condition for getting rid of eczema. Here are a few rules that will not only help you cure eczema, but also protect your body from its reappearance.
- Clothing and bedding should only be made from natural fabrics. Towels, bedding and clothes should be changed as often as possible.
- When washing, use hypoallergenic powders, rinse clothes several times.
- Try daily wet cleaning.
- Between courses of treatment, do not use hormonal ointments too often - addiction occurs in the body and the effectiveness of the drug decreases.
- When working with caustic chemicals, it is imperative to use protective equipment - respiratory masks, rubber gloves, a bathrobe.
- If open wounds appear, to avoid the formation of eczema, thoroughly disinfect damaged skin.
These simple rules will help you avoid periods of exacerbation of eczema or completely forget about the problem.
Diet is an important component of recovery
In the fight against many diseases, diet is one of the main components on the path to recovery. It is necessary to exclude provocative products from the diet - those for which there is an allergy. The most common food allergens are eggs, strawberries, chocolate, nuts, honey, citrus fruits. You should also abandon spicy, salty and smoked foods, from instant foods. Fast food, carbonated drinks, chips and salted nuts slag the intestines, which strengthens the skin rash. Nutrition should be dietary, light, healthy.
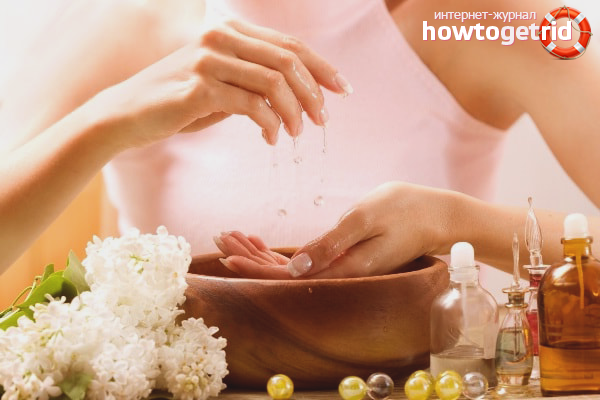
Folk remedies against eczema
In the piggy bank home medical book there are many recipes and tips that will help you in the fight against eczema.
- Salt baths. Hot salt baths are very effective for dry eczema. They disinfect the surface, relieve inflammation and itching. Pour a couple of tablespoons of salt into a liter of hot water and dissolve it. Dip your hands in the bath and keep them there for at least half an hour.
- Aloe juice and Kalanchoe. These plants have a powerful bactericidal property. Leaves can be crushed in a blender, and then squeeze the mass through cheesecloth. It is necessary to lubricate eczema with freshly prepared juice 2-3 times a day to accelerate wound healing.
- Wild strawberries. Strawberries will help relieve inflammation and burning. Fresh berries should be kneaded and applied to affected areas of the skin.
- Oil and vinegar. Any vegetable oil has a huge amount of vitamin E, which is involved in the synthesis of collagen and promotes skin regeneration. Vinegar disinfects the wound and helps remove the focus of inflammation. Mix the two components in equal proportions, soak a clean piece of gauze in the liquid, and then apply lotion to eczema for 10 minutes. Two procedures per day will be enough so that after 3-4 days the wound begins to heal.
- Sea buckthorn oil. Sea buckthorn oil perfectly helps to soften tissues during dry erosion.The oil must be preheated and applied to the affected areas of the skin.
- Vinegar, egg and water. In a glass, you need to beat one egg with the addition of 50 ml of vinegar and the same amount of water. Lubricate wet eczema before bedtime and cover with a clean cloth. In the morning, you do not need to wash off the dried film, cover it with another layer of the mixture prepared on the eve. A few days of such treatments and eczema will stop getting wet.
- Calendula, chamomile, sage. Pour one tablespoon of each plant into a liter jar. Pour boiling water over the collection, cover and let it brew for a couple of hours. When the broth cools to a warm state, lower your hands into it. Chamomile perfectly relieves inflammation and soothes the skin, sage eliminates itching and burning, calendula disinfects the surface of the wound. Such baths can be done several times a day.
- Cabbage and milk. Cabbage leaves should be carefully removed from the head, pour them with milk and put on medium heat. When the milk boils, turn down the heat and darken the leaves to make them soft. Milk leaves of cabbage should be applied to the affected skin of the hands twice a day.
These recipes are quite effective, but can only be used in combination with conservative treatment.
People suffering from eczema often feel leprosy due to the attitude of others around them. Often eczema occurs in open areas of the skin, patients have to wear gloves, sunglasses. Do not aggravate the depressed state of a patient with eczema! If there is such a person in your environment, support him with a look and a kind word, because eczema is not contagious and does not pose any danger for you. Be kinder, and the world will reciprocate!
Video: how to treat eczema








Submit